Singapore accounting & tax considerations in 2025
Since 2003, Healy Consultants Group assists our Clients with timely compliance of their annual legal, accounting and tax obligations.
-
Singapore taxation
-
Tax rates
- A company, whether incorporated in Singapore or otherwise, is considered a resident of Singapore for tax purposes if it is managed and controlled in Singapore. The corporate tax rate for resident Singapore companies is 17%. This corporate tax rate is also applicable to subsidiaries registered in Singapore and to branches of foreign companies;
- From YA 2021 onwards, there will be no corporate income tax (‘CIT’) rebate;
- There is a partial tax exemption of 75% on the first S$10,000 and 50% on the next S$190,000 of the company’s regular income from YA 2020 onwards;
- A payer must withhold tax when certain types of payments such as interest, royalty and others are made to the non-resident companies. The withholding tax rate would range from 10% to 15%. There is no withholding tax on dividends paid by company resident in Singapore;
- There is no capital gain tax and inheritance or gift tax in Singapore;
- GST is Goods and Service Tax and it is imposed on supply of goods and services by a taxable person in Singapore and on the import of goods by any person in Singapore. Standard rate of GST is 8%. Few items are exempt from GST such as goods for export and international services and sale/ lease of residential land;
- Personal income tax in the country follows a progressive system and ranges between 2% and 22%;
- From YA 2019 onwards companies will be granted a 20% Corporate Income Tax Rebate capped at $10,000;
- Currently, only group relief is available in Singapore and not tax consolidation;
- A Singapore tax resident company can enjoy tax exemption on its specified foreign income that is remitted into Singapore.
-
Goods & services tax
- A company must be registered to collect GST if its annual turnover exceeds or is likely to exceed S$1 million from the sale of taxable goods and services. This requirement may be waived if most of the goods or services are exported or supplied internationally (“zero-rated supplies”);
- Advantageous for companies to register for GST when they are having considerable amount of input GST paid on their purchases and expenses, as they will be able to claim these input GST while submitting GST returns.
- Good and Services Tax return filing and payment due date:
Quarter Due date January to March 30 April April to June 31 July July to September 31 October October to December 31 January - Late/Non-filing – IRAS will impose a late submission penalty of SG$200 immediately after the GST return filing due date. The penalty will be continuing to be imposed for every completed month when the GST return remains outstanding.
- Late/Non-Payment – A 5% of penalty will be levied on the amount of tax unpaid by the due date. An additional penalty of 2% per month on the remaining tax unpaid after 60 days from the due date.
- From January 1 2024, it will raise its GST from 8% to 9%
-
Filing due dates (corporate income tax)
Mode of Filing Filing Deadline e-Filing (Form C-S/C) 30 Nov From YA2021, all companies will be required to e-File by 30 November 2021. Paper filings will not be accepted.
-
Consequences of late / non-filing of tax returns
IRAS may take the following actions if companies fail to file the Form C-S/ C, accounts and tax computation by the due date:
- Issue an estimated Notice of Assessment (NOA). The company must pay the estimated tax within one month;
- Offer to compound the offence with a composition amount not exceeding $1,000;
- Issue a Section 65B(3) notice to the director to submit the required information in the Form C-S/ C to IRAS; and/or
- Summon the company or person responsible for running the company (including the directors) to Court.
Effective from 14 January 2022, there will be a penalty for late filing of annual lodgements beyond three months. Penalty can go up to $600.
-
Tax exemptions and rebates
If client owned bank account in Singapore with SG$ currency then they are subjected to Singapore corporate tax 17%, otherwise please provide support document or summary of transaction that show income derived from outside Singapore.
-
Nonresident companies
- A non-resident Singapore company is legally tax exempt if all of its income and profits are derived from overseas. Consequently, it can be an excellent entity to legally book global income;
- If a company is managed and controlled by directors and members residing outside of Singapore, then it is considered as a non-resident company;
- For the foreign income to be tax exempt, non-resident companies must not hold a bank account in Singapore to which the income and profits are remitted. Companies are obliged to hold international bank accounts.
- A company incorporated in Singapore but deemed as non-resident by the authorities is legally tax exempt if all income and profits are derived from overseas. Consequently, a properly structured Singapore company can be an excellent entity to legally book global income. If certain criteria are met, it is possible for the foreign income of a Singapore resident company to be legally tax exempt.
-
Resident companies
- Good news for a newly registered Singapore Companies. Entrepreneurs can now enjoy tax rebate on the profit in the first three financial years. Singapore Government exempt Private company on the following eligibility Criteria;
- Registered in Singapore;
- Tax Resident in Singapore for the given year of assessment;
- Have more than 20 shareholders consistently throughout the assessment year or at least one individual must hold at least 10% of total number of issued ordinary shares in the company.
- In order to minimize the global withholding tax, Singapore has signed 84 double taxation treaties. Singapore was one of the 68 countries that signed OECD Multilateral instrument on 7th June 2017.
- As per Income Tax Act and the Economic Expansion Incentives (EEIA), Singapore offers wide range of investment incentives including tax holidays and concessions, accelerated depreciation schemes and favourable loan conditions;
- Good news for a newly registered Singapore Companies. Entrepreneurs can now enjoy tax rebate on the profit in the first three financial years. Singapore Government exempt Private company on the following eligibility Criteria;
-
Start-ups
- To stimulate entrepreneurship, the Singapore government offers an extremely attractive tax exemption scheme for start-up companies. For the first three years, Singapore start-ups are exempt from corporate tax on the first S$100,000 and the next S$200,000 is 50% tax exempt;
- This scheme is applicable to tax resident companies that i) have less than 20 shareholders and ii) are not investment holding nor property development companies;
- Year four onwards, partial tax exemption will apply to all tax resident companies as follows: 75% on the first S$10,000 and 50% on the next S$290,000.
-
Tax rebate
Corporate Income Tax rebates are given to companies to ease their business costs and are applicable for the Years of Assessment (YAs) 2013 to 2020.The rebates apply to i) resident companies, ii) non-resident companies that are not subject to a final withholding tax and iii) companies that receive income taxed at a concessionary tax rate.
YA Corporate Income Tax Rebate Capped at 2021 & onwards No rebates $0 2020 25% $15,000 2019 20% $10,000 2018 40% $15,000 2017 50% $25,000 2016 50% $20,000 2013 to 2015 30% $30,000
-
-
Singapore tax relief and business grant schemes
As one of the world’s best places to start up a business, Singapore offers an array of tax relief schemes and small business grants. Since 2003, Healy Consultants Group has been assisting our Clients to access government incentives and support programs.
Title Base / nature Link Prerequisites Relief (based of YA2020) Tax incentives Partial tax exemption Profit before taxation See here - New start-up tax exemption was not claimed during current year of assessment (YA)
- Company must be incorporated in Singapore
75% for first
SG$10,00050% for next SG$190,000
Capped SG$102,500
New start up exemption Profit before taxation See here - Available only for first three YAs
- Company must be incorporated in Singapore
- Company must be tax resident in Singapore for that YA
- All of the shareholders are individuals or at least one shareholder is an individual holding at least 10% of the issued ordinary shares of the company
75% for first SG$100,000 50% for next SG$100,000
Capped at SG$125,000
Tax rebate Corporate tax See here All companies unless income is subject to withholding tax 25% of tax payable Capped at SG$15,000
Losses carried forward Accumulated losses carried to subsequent period See here - Only taxable expenses and income
- Can be carried forward up to 5 YAs
- Company must satisfy Shareholding Test (no substantial change in a shareholder structure)
Accumulated losses of last 5 years of assessment Losses carried back Losses of current year to claim taxes paid in a past See here - Can be carried back for one YA or three YAs (for YA 2020 enhanced carry-back relief) immediately preceding the YA in which trade losses were incurred
- Only taxable expenses and income
Capped at SG$100,000 Deductible donations Amount of donation See here Donations made to Singapore government or public for causes benefitting local community 250% of donation is tax deductible Other incentives Digital Resilience Bonus Digital improvements See here Adoption of baseline digital solutions such as PayNow Corporate and e-invoicing S$10,000 Enterprise Leadership for Transformation Education See here - Net assets or revenue more than SG$5 million
- Physical presence in Singapore
- 30% of equity held by a local
One-year programme required to develop business SkillsFuture Enterprise Credit Enterprise transformation (e g training courses, qualification programs, etc) See here - Contributes at least S$750 Skills Development Levy
- Employs at least 3 local employees
- Meets Qualifying Periods
SG$10,000 Productivity Solutions Grant Investments in high-tech and other programs / solutions to increase business productivity See here - Must have business presence in Singapore
- Purchased equipment / subscription is used for Singapore company needs
- Minimum 30% local shareholding in company
- Annual sales turnover less than S$100 million, OR less than 200 employers
Refund of up to 80% of purchase cost Enterprise Development Grant Grant to support projects within core capabilities, innovation and productivity or market access activities See here - Must have business presence in Singapore
- Minimum 30% local shareholding in company
- Approved application by ES
Grant supports up to 90% of project Other incentives See here -
Summary
A summary of Singaporean corporation tax rules include:
- A Singaporean LLC is legally exempt from all local taxes if the business has i) neither customers nor suppliers in Singapore nor ii) staff nor active directors in Singapore and iii) does not have a corporate bank account in Singapore. This non-resident LLC cannot benefit from double taxation treaties.
- A Singaporean LLC is tax resident when the business in managed from Singapore including i) the majority of shareholders and directors reside in Singapore or frequently travel to Singapore to oversee local business activities, including attending Board meetings and ii) has a multi-currency corporate bank account in Singapore. A tax resident LLC enjoys the benefits of double taxation treaties and local government grants and tax incentives.
-
-
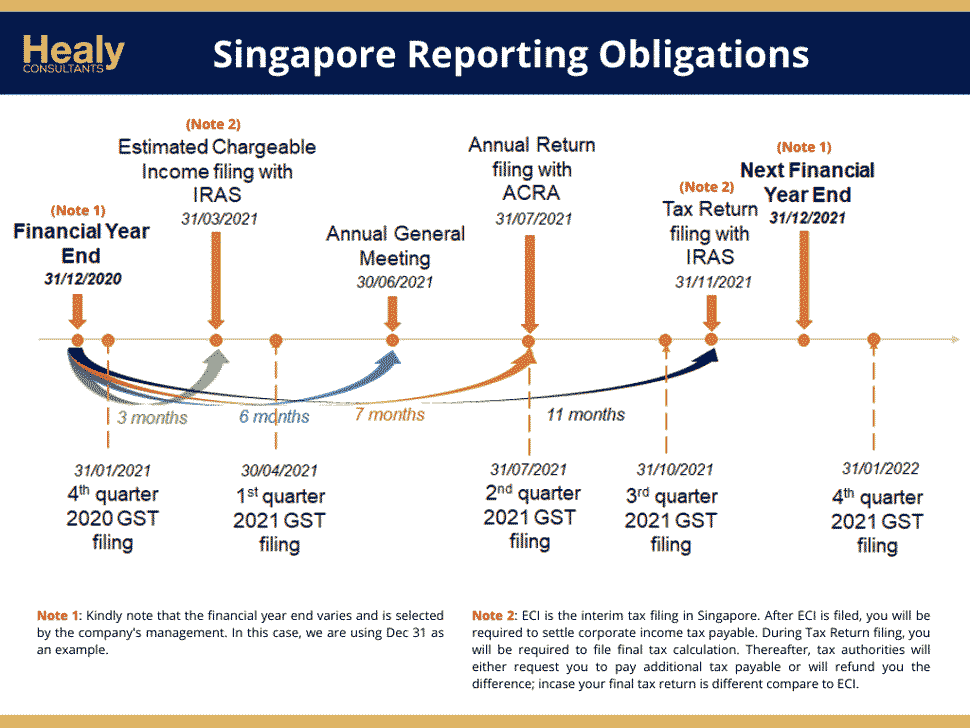
Tax reporting, accounting and auditing considerations
- Annual return and income tax returns are filed online.
- The corporate tax filing deadline for all Singapore companies is 30 November every year.
- It’s compulsory for all companies to prepare a financial statement within six months of the company FYE in accordance with Singapore Reporting Standards.
- Dormant and small companies are exempt from an audit if they fulfil the following conditions:
- They are a private company (owned by 50 members or less) for the financial year.
- They meet at least two of the following three quantitative criteria for the immediate past two financial years:
- Total revenue not more than S$10 million
- Total assets not more than S$10 million
- Total number of employees not more than 50
- All Singapore companies must register for GST if annual sales exceed or are expected to exceed S$1 million.
- Late filling penalty for a Singapore company is S$300. Fr the subsequent 3 months, the late penalty doubles to S$600.
- If a company does not fulfil its accounting and tax obligation, it can be struck off by the Singapore authorities as per the Singapore Company Act.
-
Consolidated financial statement
- According to the Singapore Accounting Standards, a parent entity that controls more than one entity required to prepare consolidated financial statement.
- However, the parent entity is exempted from preparing a consolidated financial statement if it meets all the following requirements:
- a wholly owned subsidiary or partially owned subsidiary of another entity and all other owners have been informed and do not object to the parent not presenting the consolidated financial statement;
- its debt or equity instrument are not traded in the public market;
- it didn’t file nor in the process of filing its financial statement with the securities commission or other government authorities for the purpose of issuing any class of instrument; and
- its ultimate or intermediate parent prepare financial statement that are available for public.
-
Singapore company tax exemption package
- A properly structured Singapore company can be legally tax exempt if certain criteria are met;
- Press this tab to view a sample draft invoice for our standard Singapore offshore package.
View PDF
-
Compare different Singapore entities
No Question Tax resident LLC Offshore company Non-resident taxable LLC 1 Must pay Singaporean corporation tax of 17%? Yes No Yes 2 Corporate bank account location In Singapore Outside Singapore In Singapore 3 Management and control of entity In Singapore Outside Singapore Outside Singapore 4 Practical example Healy Consultants Singapore Pte Ltd A US-based Client owns a Singapore LLC and Hong Kong bank account A US-based Client owns a Singapore LLC and DBS Singapore bank account 5 Annual net profits tax exemption bracket The first SG$125,000 of annual net profits are tax free for first 3 years. Anything over this SG$ amount is taxed at 17% Legally tax exempt on all profits The first SG$102,500 of annual net profits are tax free. Anything over this SG$ amount is taxed at 17% 6 Access to double tax treaties? Yes No No 7 Can obtain a tax resident certificate? Yes No No 8 Can open a Singapore merchant account? Yes No Yes 9 Access to Government grants and incentives? Yes No No 10 An excellent holding company of global subsidiaries? Yes No No 11 Can have a virtual office with call answered from Singapore? Yes Yes Yes 12 Can hire staff in Singapore? Yes No Yes Detail
- A Singapore LLC pays local corporation tax when i) business is done in Singapore or ii) management and control is within Singapore or iii) it has a Singapore corporate bank account.
- A Singapore LLC is legally tax exempt if i) it has no staff or active directors in Singapore ii) no customers or suppliers in Singapore iii) no Singapore corporate bank account. This is known as a Singapore offshore company.
- Usually, IRAS will only classify a company as tax resident and supply it with a tax residency certificate if the business can demonstrate that it is controlled and managed in Singapore. For example, Healy Consultants Group Singaporean companies. However, merely i) appointing nominee Singaporean directors or ii) having a local virtual office is not sufficient to be a tax-resident business.
- An offshore Singapore LLC will pay Singapore corporation tax if i) sales closed with Singaporean customers or ii) overseas sales are banked to a Singapore bank account. Also known as non-resident LLC.
- On a separate note, a statutory audit of the financial statement of a Singapore company is required if such business exceeds at least two of the following thresholds: i) annual sales over SG$10 million ii) assets over SG$10 million iii) more than 50 employees. In case a company has corporate shareholders or subsidiaries, these thresholds apply at the Group level, not only at the entity level.
- For a taxable Singaporean LLC, overseas income is legally tax exempt if not remitted to a Singapore multi-currency corporate bank account.
- Sales received through a Singapore merchant account is legally tax exempt if those funds are transferred to an overseas corporate bank account, and not remitted to a Singapore multi-currency corporate bank account or used to settle liabilities in Singapore.
-
Healy Consultants Group fees for accounting and tax support
Singapore accounting and tax task US$ Singapore active company unaudited annual tax and accounting 2,700 Singapore dormant company unaudited annual tax and accounting 1,200 Singapore active company audited annual tax and accounting * 7,750 Singapore annual personal tax return 1,950 Singapore company residence certificate 950 IRAS written confirmation of legal tax exemption 1,500 Average monthly bookkeeping services 550 Quarterly GST reporting services (active entity) 950 Quarterly GST reporting services (dormant entity) 450 Note: * For an active trading company, these accounting, audit and tax fees are an estimate of Healy Consultants Group fees to efficiently and effectively discharge your annual company accounting and tax obligations. Following receipt of a set of draft accounting numbers from your company, Healy Consultants Group will more accurately advise accounting and tax fees
-
Maintaining accounting, secretarial and corporate structure data
- Entities should maintain proper books of accounts and also record all invoices and receipts for their company expenses and income. The same can be required at any time by the Singapore authorities;
- Entities should also maintain the secretarial records such as board resolutions and meeting minutes of all the important management decisions taken by the Directors;
- Under Singapore legal system for business, the information related to the corporate structure such as shareholders, directors, shares and secretaries is centralized by the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority’s bizfile system. However, any change in the corporate structure of the entity must be immediately notified to secretary of the entity for updating of the ACRA records.
-
Amendment in tax return
In the unlikely case of a tax filing mistake, a company’s management is required to file notice using the Voluntary Disclosure Programme (VDP). The notice should be submitted as soon as the mistake is identified. Timely action will significantly help reduce potential penalties and the IRAS officer’s treatment of your case. -
Estimated chargeable income (ECI) filing
- Starting from the Year of Assessment 2020, all companies are required to file Estimated Chargeable Income within three months of the financial year end. For more details about exemptions, refer to this website.
- The Singapore government does not impose any late filing penalties assuming the tax return (Form C, Form CS or Form CS Lite) has been done on time.
- Your company does not need to file ECI in any Year of Assessment (YA) when both of the following criteria are met:
- Annual revenue is $5 million or below for the financial year; and
- ECI is nil for the YA. The ECI should be the amount before deducting the exempt amount under the partial tax exemption scheme or the tax exemption scheme for new start-up companies.
-
Notice Of Error (NOE)
- Clerical/typographical error: This NOE option is for errors contained in the filed document that were unintended and do not harm or mislead any person(s). The (non-refundable) government fee is S$60 (click link).
- Applications to Registrar for other errors: This NOE option is for errors contained in the document filed that were unintended and do not prejudice any person(s). The (non-refundable) government fee is S$60 (click link).
- Notification of revised financial statements: This NOE option is to re-file the company’s financial statements which have been revised to correct non-compliance(s) with the requirements of the Companies Act and accounting standards. The (non-refundable) government fee is S$ 200 (non-refundable) (click link).
-
Frequently asked questions
-
When are financial statements prepared and submitted to ACRA?
All Singapore companies, except solvent Exempt Private Companies (EPC) must file financial statements with ACRA.
An EPC is a Singapore company which has i) less than 20 shareholders and ii) none of the shareholders is a corporate entity.
-
When are financial statements prepared and submitted to IRAS?
All companies must submit financial statements to IRAS if they meet the following criteria: i) annual revenue higher than SG$5 million ii) claiming carry-back of capital allowances/losses iii) applying for group relief iv) applying for investment allowance and v) claiming a foreign tax credit. -
When must a company submit a corporation tax return to IRAS?
All Singapore companies must a corporate tax return for the financial year by i) 30th November of the following year (paper filing) or ii) 15th December of the following year (e-filing). -
When are consolidated financial statements required?
If a Singapore company is the ultimate holding company for one or more entities (subsidiaries), it must prepare consolidated financial statements (See SFRS 110). -
When is independent statutory annual audit required?
If a Singapore company meets 2 out of the following 3 requirements for two consecutive financial years: i) revenue > SG$10 million ii) assets > SG$ 10 million or iii) employees > 50, then audit is required. -
When are audited consolidated financial statements required?
If a Singapore company must prepare consolidated financial statements and the Group consolidated financial statements meet the audit requirements mentioned in the question above, then audited consolidated financial statements are required. -
When are financial statements not required to be prepared and not submitted to ACRA?
Under Section 201 of the Companies Act, all Singapore companies must prepare financial statements, no exceptions. However, if the company is a solvent EPC (see question 1), it may not submit the financial statements to ACRA. -
When are financial statements not required to be prepared and not submitted to IRAS?
All Singapore companies must prepare financial statements annually. However, if the company does not meet any of the 5 requirements mentioned in question 2, it is not required to submit the financial statements to IRAS. In such a case, it will only need to file Form C-S. -
When are consolidated financial statements not required?
A Singapore parent company need not prepare consolidated financial statements if it meets all the following conditions:
- It is a wholly-owned subsidiary or a partially-owned subsidiary of another entity;
- Its debt or equity instruments are not traded in a public market;
- It has never been required to file financial statements with a regulatory authority for issuing financial instruments in a public market; and
- Its ultimate or any intermediate holding company produces financial statements available for public use that comply with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
-
When is an independent statutory annual audit not required?
An independent statutory annual audit is not required if a Singapore company does not meet 2 out of the following 3 requirements for two consecutive financial years: i) revenue > SG$10 million ii) assets > SG$ 10 million or iii) employees > 50, then audit is required. -
When are audited consolidated financial statements not required?
Audited consolidated statements are not required if a Singapore parent company meets all the requirements detailed in question 9 and 10. -
For a Singapore holding company, when are entity level financial statements required to be submitted to ACRA and IRAS?
ACRA and IRAS guidelines do not differentiate between a normal company or holding company. Consequently, a Singapore holding company must submit financial statements to ACRA and IRAS if it meets all the requirements in question 1 and 2. -
What is the benefit to have a holding company?
A holding company may enjoy the following benefits:
- Receive withholding tax on dividends, if DTAA is signed;
- Legally minimize international tax on other passive income including royalties and IP;
- Reduce risk exposure to assets of the existing company;
- Conduit to raise capital and transfer it to the existing business;
- Prepare for an Initial Public Offering (IPO).
For further details, please refer to our detailed holding company webpage.
-
How long must companies keep their financial and accounting and tax records?
According to local legislation a company should maintain proper records for a minimum of five calendar years, and must be able to provide necessary information to government authorities upon request. -
Are there any due dates to object to the IRAS tax assessment?
Following receipt of Notice of Assessment from IRAS, the company’s management has two months to raise an objection. The assessment will be considered final if no objection is received during this period. -
What is the best way to contact IRAS?
IRAS has a live chat function on its website, operational Monday-Friday, 8am-5pm, Singapore time. Live chat is a much faster way to communicate with an IRAS officer than calling or e-mailing general enquiries, and you are likely to get an instant response.
-
-
Related videos / podcasts
-
Accounting & annual tax return filing obligations for a dormant company in Singapore
-
Singaporean company annual renewal for a USA Client
-
-
Useful links
-
External readings
It is important for our Clients to be aware of their personal and corporate tax obligations in their country of residence and domicile to fulfill those obligations annually. Let us know if you need Healy Consultants Group’s help to clarify your annual reporting obligations.